Is MIG Welding Safe and Effective for Pros and Hobbyists?
July 29, 2021

As technology continues to evolve, metal inert gas (MIG) welding ranks as an industry-standard method. Because it leverages agile equipment and materials, MIG welding remains a darling among professionals and hobbyists alike. By that same token, MIG welding flexibility sometimes makes users feel more comfortable than safety dictates. If you are interested in adding a setup to your business or employing it for practical and creative endeavors, these are essential things you should know about MIG welding.
What is MIG Welding?
What distinguishes MIG welding from other forms of metal joinery is the gas-driven arc used in this method. Also known as gas metal arc welding, the respective metal items are heated with a fiery arc fed a filler electrode. This style of welding also employs a shielding gas that secures the molten pool of material against elements in the surrounding environment that might taint it. To better understand how MIG welding works, people interested in taking up the craft would be well-served to familiarize themselves with the following industry terms.
- Parent Metal: This material involves the two or more metals a welder plans to join together.
- Filler: This material is typically added during the welding process to fuse the parent metal.
- Weld Metal: This encompasses the heated metal that melts and is retained in the weld throughout the joining process.
- Heat Affected Zone: Also called the “HAZ” by experienced welders, this entails the metal impacted by the process that does not necessarily melt. It’s part of metal that often gets hot and may undergo metallurgical changes.
Effective MIG welding requires a Direct Current Positive Electrode, typically known as Reverse Polarity. This connects the metal to a power source’s negative terminal and an electrode to a positive one. The inherent difference forces electrons to accelerate at high velocity, and kinetic energy is rapidly converted to thermal energy, aka heat.
What is MIG Welding Used For?
This style of welding remains popular because it offers wide-reaching flexibility. Users can employ the process to expedite repairs to automobile bodies, farm equipment, gates, railings, bicycles, motorcycles, boats, and artists routinely learn MIG welding to create sometimes large-scale metal sculptures. Because MIG welding tools and equipment are relatively easy to move, it remains a flexible metal joining option for professionals and hobbyists alike.
What are Top MIG Welding Safety Concerns?
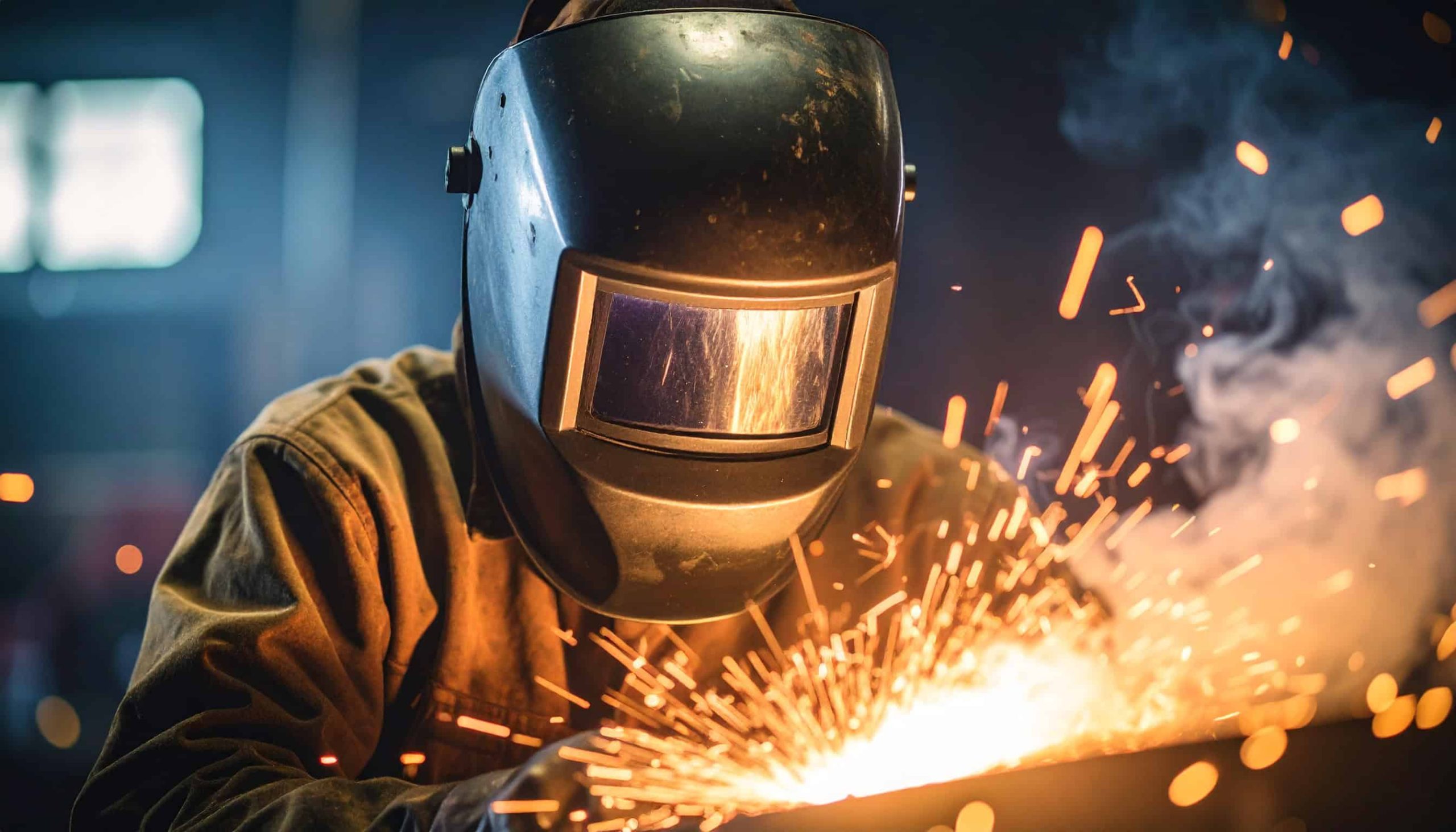
To say that MIG welding safety is job one would be something of an understatement. This metal joining process reaches temperatures upwards of 3,000 degrees, and a single misstep can result in significant injuries. In addition, the arc itself can achieve temperatures exceeding 15,000 degrees. That’s why it’s critical for upstart welders and seasoned veterans alike to use best practices regarding hazards that include the following.
- Risk of Fire: A wide range of hot work activities surrounds the MIG welding process. It’s crucial to protect yourself, bystanders and ensure potentially flammable materials are kept at a safe distance.
- Respiratory Dangers: During the metal joining process, raw materials are effectively vaporized. These usually include toxic fumes from the filler material, metal, and products such as paint. Welders and people in the surrounding area are tasked with preventing hazardous vapors from entering their lungs.
- Arc Flash: The intensity of MIG welding is so bright that it can damage the eyes. Looking directly at the arc almost always negatively impacts sight. Sometimes more concerning is arc flash occurring from peripheral vision.
- Burns: The molten materials involved in MIG welding can splatter, and the temperature of parent metal soars. Too many welders learn the safety risk the hard way after sustaining burns.
It’s also not unusual for the extreme ultraviolet light generated during the MIG process to cause sunburn on anyone with exposed skin in the weld zone. In addition, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) helps reduce the risk of ergonomic-related injuries such as strained neck muscles and joints.
What are Safety Tools Needed for MIG Welding?
Anyone who wants to start MIG welding will require two distinct sets of tools. On the one hand, you will need items necessary to effectively join parent metals together. The other set involves selecting industry-leading PPE to ensure safety during every weld. The following rank among the essential PPE.
- Welding Helmet
- Welding Jacket
- Welding Gloves
- Safety Glasses
- Ear Protection
- Grinding Visor
- Steel Toe Work Shoes
- Fire Extinguisher
The PPE welding enthusiasts select should also be synced with what is known as a “shade rating,” which corresponds to the MIG heavy or light metal measure. It’s generally in a welder’s best interest to conduct some due diligence or talk to a MIG welding expert when choosing PPE.
Contact the Leading MIG Welding Supplier in Arizona
The professionals at Vern Lewis Welding Supply hope this MIG information proves useful. We maintain a complete inventory of industry-leading MIG welding supplies, PPE and offer a wide range of services, as well as educational resources. If you have questions regarding MIG welding, contact one of our eight locations for more information.
Sources:
- https://weldingheadquarters.com/what-does-dcep-mean-in-welding/
- https://www.hagerty.com/media/maintenance-and-tech/15-must-have-mig-welding-tools/
- https://weldingheadquarters.com/what-is-mig-welding/
- https://ehsdailyadvisor.blr.com/2014/11/identify-the-5-most-common-hazards-of-mig-welding/
- https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/job-knowledge/equipment-for-mig-welding-015
- https://welditmyself.com/what-is-mig-welding-used-for/
- https://www.wasatchsteel.com/advantages-mig-welding/
Join Our Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter to receive specials offers, product updates, and more!