Welding Porosity Explained: Causes, Types, and Prevention
October 8, 2025

Welding aims to create strong, dependable joints — but even the most visually perfect welds can hide flaws below the surface. One of the most common and potentially serious defects is welding porosity. These small gas pockets or voids inside the weld metal may look insignificant, yet they can weaken the joint, cause failures, and result in expensive repairs.
In this article, we’ll cover what welding porosity is, why it happens, the main types you might encounter, and how to prevent it.
What Causes Welding Porosity
Porosity forms when gas becomes trapped in the molten weld pool and cannot escape before the metal solidifies. This leaves holes either visible on the surface or hidden within the weld. Common causes include:
- Contaminants on the base metal or filler – Oil, paint, rust, or mill scale can release gases when heated, which then become trapped in the weld.
- Moisture in materials or shielding gas – Water breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen under heat, leading to porosity and possible hydrogen-induced cracking.
- Poor shielding gas coverage – Drafts, incorrect flow rates, or damaged nozzles can allow oxygen and nitrogen into the weld zone.
- Incorrect welding parameters – Excessive arc length, wrong travel speed, or mismatched settings can increase the chance of gas entrapment.
Knowing these causes is the first step in preventing porosity.
Types of Porosity
Porosity can present in different forms, and identifying the type can help pinpoint the source:
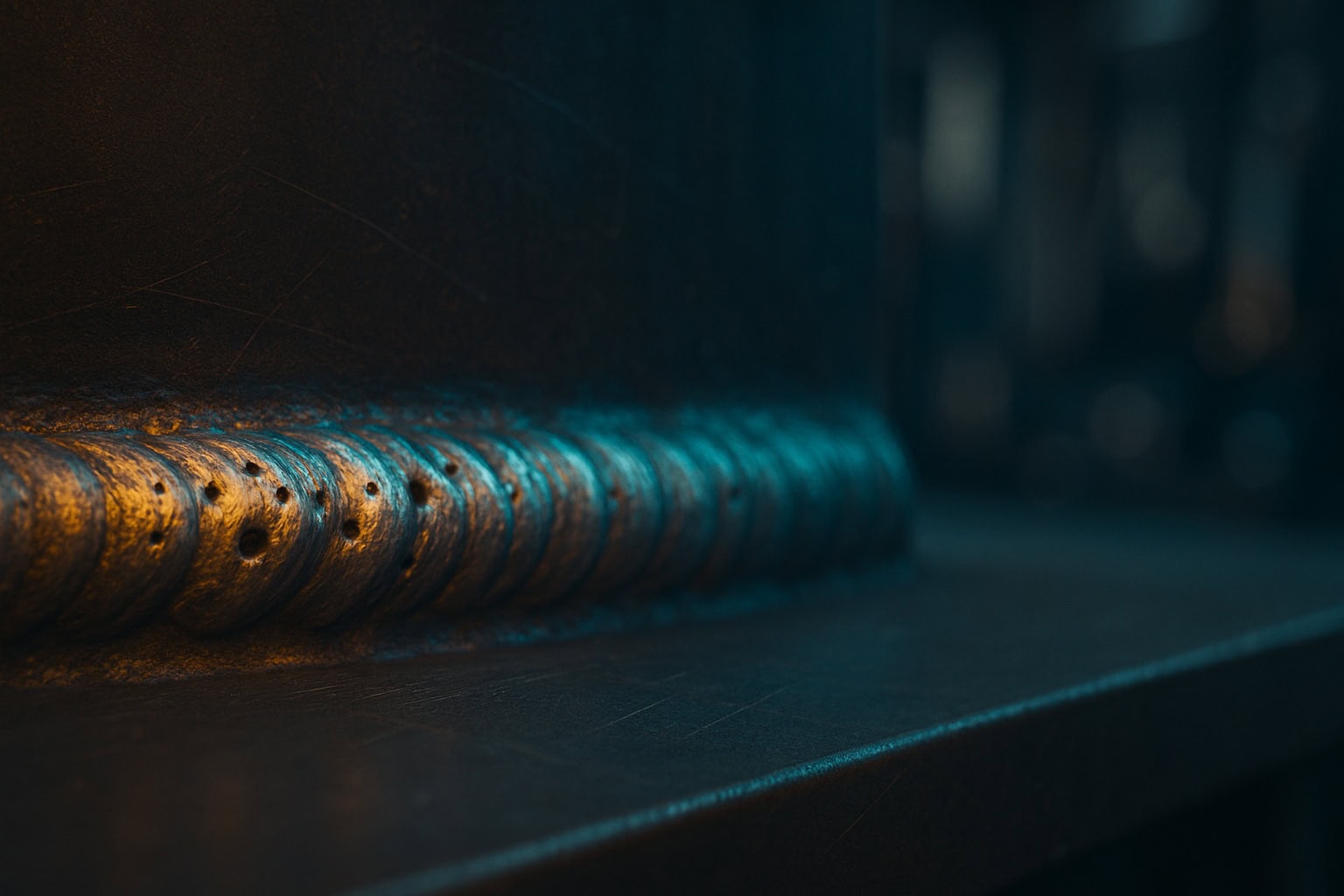
- Surface porosity – Visible pits or holes on the weld bead, often due to contamination or inadequate shielding.
- Subsurface porosity – Hidden flaws found using non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or radiographic inspection.
- Cluster porosity – A group of small pores in one area, usually from localized contamination or sudden loss of shielding gas.
- Wormhole porosity – Elongated voids caused by gas escaping late in the solidification process.
Effects on Weld Quality
Even small amounts of porosity can affect performance. The most immediate concern is reduced strength. Gas pockets replace solid metal, leaving less material to bear the load. In critical applications such as pipelines, pressure vessels, or structural components, this can greatly increase the risk of premature failure.
Porosity also creates stress points, making welds more likely to crack under repeated loads or environmental stress. Beyond structural risks, porosity often results in costly rework and downtime, especially if detected after the weld is complete.
Welding codes and standards set strict limits on acceptable porosity. In many industries, even small defects require grinding out and re-welding the affected area.
How to Prevent Welding Porosity
Most porosity issues can be avoided with proper preparation and technique. Key prevention measures include:
- Clean materials thoroughly – Remove oil, paint, rust, moisture, and mill scale before welding.
- Store and handle consumables correctly – Keep electrodes, filler rods, and fluxes dry and free from contamination.
- Ensure correct shielding gas type and flow – Match gas to process and material, set proper flow rates, and check for leaks or drafts.
- Follow correct welding procedures – Maintain recommended travel speed, arc length, and torch angle, and use parameters suited to the base and filler materials.
- Inspect equipment regularly – Keep cables, hoses, regulators, and torches in good condition for consistent gas coverage and performance.
A few minutes of preparation can mean the difference between a flawless weld and one that fails inspection.
Conclusion
Welding porosity may be small, but its impact on strength, safety, and cost is significant. Understanding its causes, recognizing the types, and applying prevention best practices greatly reduces the chance of this defect. Defect-free welds come from attention to detail, thorough preparation, and consistent technique.
Join Our Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter to receive specials offers, product updates, and more!